 Meniscus Magazine is here to support the mind expansion side of health and wellness, this time we’re talking about nutritional neuroscience. But before we get into that, in order to understand how to supplement the brain with different compounds, it is important to understand the basic functioning of the grey area.
Meniscus Magazine is here to support the mind expansion side of health and wellness, this time we’re talking about nutritional neuroscience. But before we get into that, in order to understand how to supplement the brain with different compounds, it is important to understand the basic functioning of the grey area.
The brain consists of millions of cells known as neurons. The function of these cells is to fire a neurotransmitter into the synapse. The synapse is a gap between the two nerve cells that when bridged by a neurotransmitter, will trigger the next neuron to fire. Think of it a bit like dominoes falling sequentially after the first one is knocked over.
The difference is, once the neuron fires to activate the next link in the chain, the neurotransmitter is sucked back into the nerve in what is called re-uptake. This is analogous to each domino popping back up ready for the next fall.
Within each neuron is a delicate system of electrical balance. This mechanism is at the very foundation of every action your body plays out, voluntary or otherwise.
Nutritional Neuroscience
Many factors can contribute to how well your brain functions chemically. Of course there are many genetic, emotional and environmental factors that affect the brain dramatically, but for this discussion, let’s focus on the chemical science going on. (We will save neuroplasticity for another conversation..) With a quick trip to the health food store, you can give one of your most precious organs a revitalizing dose of nutrients. Here is a short list of some common mind drugs.
(Note: These statements are based on research and personal experience and have not been evaluated by the FDA—or anyone for that matter!—and are purely intended as food-for-thought.) (No pun intended.)
Circulation enhancers
 - Ginkgo biloba – One of the most common brain boosters, ginkgo is a tree thought to be several thousand years old. It helps the brain receive oxygen from the circulatory system by dilating the capillaries in the brain thus allowing for more red blood cells to nourish brain cells.
- Ginkgo biloba – One of the most common brain boosters, ginkgo is a tree thought to be several thousand years old. It helps the brain receive oxygen from the circulatory system by dilating the capillaries in the brain thus allowing for more red blood cells to nourish brain cells.
Ginkgo is also a powerful anti-oxidant, a helpful defender of free radicals which contribute to sickness and disease.
Antioxidants
 - Powerful anti-oxidants help the brain ward off old age by countering enemy free radicals. These are best consumed in a diet rich in leafy green vegetables and fresh berries. Here are some of the main groups:
- Powerful anti-oxidants help the brain ward off old age by countering enemy free radicals. These are best consumed in a diet rich in leafy green vegetables and fresh berries. Here are some of the main groups:
– Vitamin E (20,000 iu): Broccoli, carrots, nuts, papaya, pumpkin, red peppers, spinach, and sunflower seeds.
– Vitamin C (100-500 mg): Berries, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, grapefruit, honeydew, kale, mangoes, peppers, sweet potato and tomatoes.
– Cardenoids (Beta-carotene): Apricots, asparagus, beets, broccoli, carrots, corn, kale, mangoes, collard greens, spinach, sweet potato and watermelon.
– Selenium (20-100 micrograms):
– Flavonoids and Glutathione.
Serotonin enhancers
 - Created by brain cells and stored in vesicles, the neurotransmitter serotonin affects mood, arousal, aggression and clear thinking.
- Created by brain cells and stored in vesicles, the neurotransmitter serotonin affects mood, arousal, aggression and clear thinking.
Enhancing levels can serve as an antidepressant but will also sedate and lower sex drive. Predecessors include meat, fish and other protien foods. At night the pineal gland converts serotonin to melatonin which aids sleep.
5HTP, St. John’s Wort, Prozac.
Mind Energizers
 – Can affect alertness, arousal, vigilance, mood, energy, motivation, concentration, focus, verbal fluency, visual enhancement.
– Can affect alertness, arousal, vigilance, mood, energy, motivation, concentration, focus, verbal fluency, visual enhancement.
A very basic enhancer, vitamin B allows the body to convert food to energy. Specifically if you are a vegetarian, you may need to supplement B-12 as it is typically found in meats and some fish. Adding B-vitamins to your diet will affect mood, energy, alertness, learning, memory, verbal fluency, concentration, focus and vision.
Brain Hormones
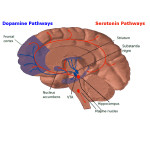 – Many brain hormones are synthesized from cholesterol. Stress and changes in our biological clocks can affect your chemistry and can influence memory, sex drive, mood and levels of energy. May even affect creativity and overall awareness.
– Many brain hormones are synthesized from cholesterol. Stress and changes in our biological clocks can affect your chemistry and can influence memory, sex drive, mood and levels of energy. May even affect creativity and overall awareness.
As the production of such hormones decreases with age, it may be helpful to supplement them as the body ages. Includes supplements such as pregnenalone, the precursor to several different brain hormones.
Choline
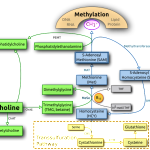 – A predecessor to acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter that helps with learning, focus and memory. Increasing the supply will result in a perceptible enhancement in focus. Another way to increase levels of choline is to take an herb such as Huperzine A which reduces the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which breaks down acetylcholine.
– A predecessor to acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter that helps with learning, focus and memory. Increasing the supply will result in a perceptible enhancement in focus. Another way to increase levels of choline is to take an herb such as Huperzine A which reduces the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, which breaks down acetylcholine.
Choline is found in fatty meats and fish, so again if you are a vegetarian, you may need to add a supplement.
Methyl Donors
 – This is another related chemical reaction where supplements will provide an additional methyl molecule that assist in the production of several substances in the brain.
– This is another related chemical reaction where supplements will provide an additional methyl molecule that assist in the production of several substances in the brain.
Affect mood, energy, well-being, alertness, concentration, visual clarity, sexual well-being, and may help prevent age-related cognitive decline: DMAE & SAMe.
Omega 3 fatty acids
 – This is something that not only affects the brain, but is also a powerful tool against inflammation.
– This is something that not only affects the brain, but is also a powerful tool against inflammation.
Affect mood, clarity, serenity, mental stability, concentration and focus, vision: Fish or flax seed oil (1 tbsp each or around 1 gram), also contains phospholipids.
Please use caution and research this information on your own before experimenting with your own nutritional neuroscience. This summary is for your information only. You’re on your own, enjoy experimenting with your control group!
by Jon Heinrich
Bibliography:
Sahelian, Ray, “Mind Boosters: A guide to natural supplements that enhance our mind, memory, and mood.” St. Martin’s Griffin, New York, 2000.
Feature image used from Scientopia under fair use, educational purposes
Images used from Wikimedia Commons:
Human brain showing energy consumption
Wild Alaska Berries
Serotonin
Mind energy
Hormones
Choline metabolism
Methyl donors
Omega 3 fatty acids (flax seeds)
Leave a Reply